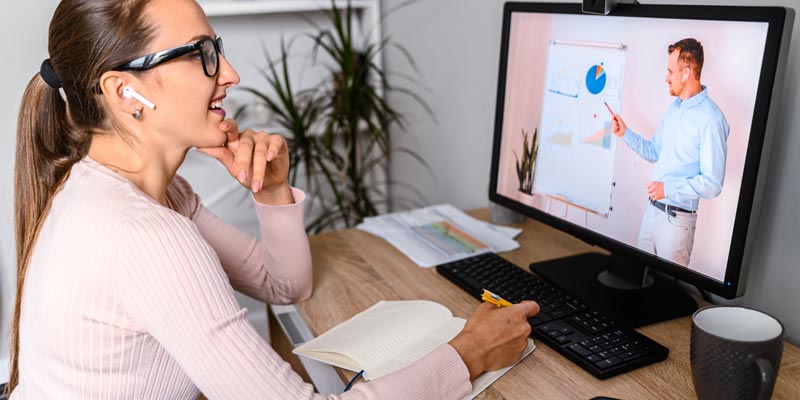
FDA 21 CFR Part 11 is the FDA guideline that defines the criteria under which electronic records and electronic autographs are considered to be secure, dependable and original to that of the paper records. FDA 21 CFR Part 11 Part 11, as it’s generally known, was introduced in 1997 and applies to FDA- governed diligence that choose to store their primary, FDA 21 CFR Part 11authoritative records electronically. It stipulates the guidelines and rules for storehouse, copying, access & warrants, inspection logs & shadowing. It also identifies interpretation control of the electronic records and the operation of electronic autographs to them.
Part 11 applies to all records that are defined in the underpinning Acts and Regulations which govern conditioning in the life lores diligence. Part 11 requires medicine makers, Medical Bias manufacturers, biotech companies, biologics inventors, and other FDA- regulated diligence to apply controls, including checkups, system attestations, inspection trails, electronic autographs, & attestation for software and systems involved in processing electronic data that are moreover needed to be maintained by the FDA predicate rules or used to demonstrate compliance to a predicate rule.

Compliance Quest (CQ) supports 21 CFR Part 11 FDA compliance conditions for life lores associations in health- care, medicinal, life- wisdom, biotechnology, medical-manufacturing, medical bias, and other FDA- regulated diligence. Title 21 CFR Part 11 requires companies to apply controls, including checkups, system attestations, inspection trails, electronic autographs, and attestation for FDA 21 CFR Part 11 software and systems that are involved in processing numerous forms of data, as part of their business practices and product development.
Title 21 CFR Part 11 legislated the FDA’s demand that they’re suitable to fete electronic records and electronic autographs as secure, FDA 21 CFR Part 11 dependable, and legal coequals to paper records and handwritten autographs. This also allows companies to borrow a’paperless’ system of record keeping.
Electronic Hand
CQ automatically secures and binds the authenticated stoner’s electronic hand. CQ ensures that the stoner has inked onto the system and exposed their hand via the forced authentication process, FDA 21 CFR Part 11 as needed by 21 CFR Part 11. Authentication is needed each time a sale is reused which is original to that of a paper form that would have been inked by an existent.
Inspection Trail
CQ securely and automatically posts all field changes to a separate database. The Inspection Trail includes the field’s old value, new value, name of the stoner who made the change, and date and time. CQ not only stores the inspection trail information but also allows for the information to be queried and help present the information to support a nonsupervisory inspection.
UNDERSTANDING THE REGULATORY Conditions OF 21 CFR 11
It’s imperative you understand the nonsupervisory conditions for both 21 CFR 11 and the commerce with the applicable predicate rule, else you’ll have problems enforcing an effective approach for Part 11 compliance. Likewise, the compliance policy companion sets out the FDA’s prospects when they check a pharmaceutical company. This donation will explain in detail
Counteraccusations of the final rule and how it affects day to day practice-what are the real issues and how to deal with them.
Electronic records and closed systems defined and what they mean
Electronic records and their operation and how 21 CFR 11 will affect
Open and closed systems
Security and access control issues
The use of mongrel systems ( paper autographs and electronic records)? What systems produce electronic records and are governed by 21 CFR11?
Perpetration AND Confirmation OF NEW SYSTEMS-1 Conditions, SPECIFICATIONS AND EVALUATION
.If you need to replace or modernize a system what are the benefits you can gain from 21 CFR 11? Should you replace like FDA 21 CFR Part 11 with like or redesign to take advantage of the regulation?
Look at your process and computer confirmation conditions can you ameliorate the process and gain benefits from working electronically as well as FDA 21 CFR Part 11 reducing your confirmation workload?
What are the specification needs and the possible problems associated with
The system conditions
Electronic records/ electronic hand (ER/ ES) conditions
How to estimate the new system/ operation
Electronic Records and Electronic Autographs (21 CFR 11) Conditions
Perpetration AND Confirmation OF NEW SYSTEMS-2 QUALIFICATION
Qualification of the system has always been a specific demand for confirmation of a system. With the emergence of 21 CFR.